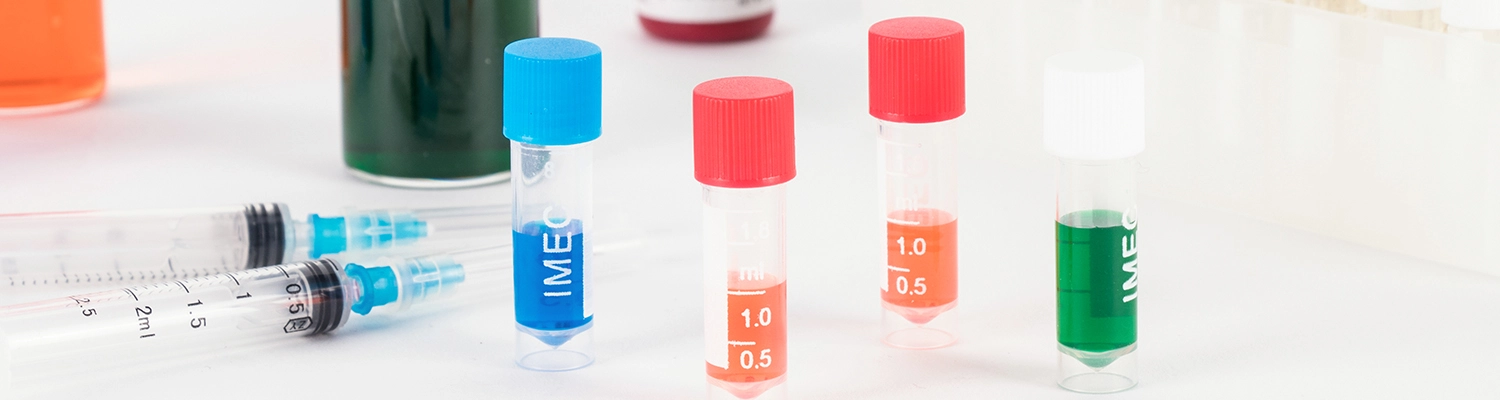
How Does Polyvinylpyrrolidone Iodine Work as a Broad-Spectrum Antiseptic?
Polyvinylpyrrolidone Iodine (PVP-I), commonly known as povidone-iodine, represents one of the most effective and widely used antiseptic agents in modern medicine. This comprehensive guide explores the sophisticated mechanism through which PVP-I achieves its remarkable broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. We examine the chemical synergy between polyvinylpyrrolidone and iodine, analyze its applications across healthcare sectors, compare its efficacy with other antiseptics, and review safety protocols. With insights into manufacturing standards from leading producers like Xiamen Aeco Chemical Industrial Co., Ltd., this article provides healthcare professionals, researchers, and industry experts with essential knowledge about this indispensable infection control agent.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- 1. What is the Chemical Mechanism Behind PVP-I's Antimicrobial Power?
- 2. How Extensive is PVP-I's Antimicrobial Spectrum and Efficacy?
- 3. Where Are the Most Critical Applications of PVP-I in Modern Healthcare?
- 4. What Key Advantages Does PVP-I Offer Over Alternative Antiseptics?
- 5. How Should PVP-I Be Safely Applied in Clinical Settings?
- 6. How is High-Quality PVP-I Manufactured and Controlled?
- 7. What Future Developments Are Expected for PVP-I Technology?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the Chemical Mechanism Behind PVP-I's Antimicrobial Power?
The remarkable efficacy of Polyvinylpyrrolidone Iodine stems from a sophisticated chemical partnership between its two components: the polymer polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and elemental iodine. Unlike simple iodine solutions, PVP forms a stable complex with iodine, creating a reservoir that releases free iodine gradually and consistently.
The PVP polymer acts as a carrier and sustained-release vehicle for iodine. This complex dissociates in aqueous environments, releasing free iodine at concentrations that remain consistently microbicidal without reaching levels that would cause tissue irritation.
Molecular Action Against Pathogens
Once released, free iodine attacks microorganisms through multiple simultaneous mechanisms:
| Mechanism | Target | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation | Sulfhydryl (-SH) groups in proteins and enzymes | Disruption of protein structure and enzyme inactivation |
| Halogenation | Nucleotide bases in DNA/RNA | Impairment of nucleic acid synthesis and replication |
| Membrane Disruption | Lipid bilayers and cell walls | Increased permeability and cellular content leakage |
| Enzyme Complexing | Active sites of critical microbial enzymes | Irreversible inhibition of metabolic pathways |
This multi-target approach explains why microorganisms rarely develop resistance to PVP-I—mutations would need to simultaneously protect against multiple mechanisms of action.
How Extensive is PVP-I's Antimicrobial Spectrum and Efficacy?
PVP-I demonstrates exceptional breadth in its antimicrobial coverage, making it one of the few agents effective against all major pathogen classes. The spectrum includes both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, mycobacteria, bacterial spores, fungi, protozoa, and both enveloped and non-enveloped viruses.
Contact Time and Efficacy Relationships
One critical factor in PVP-I's effectiveness is the required contact time, which varies by microorganism type:
| Microorganism Type | Typical Log Reduction | Recommended Contact Time | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-positive Bacteria (S. aureus, S. pyogenes) | 4-5 log10 (99.99-99.999%) | 15-30 seconds | Surgical scrubs, wound care |
| Gram-negative Bacteria (E. coli, Pseudomonas) | 4-5 log10 | 30-60 seconds | Medical device disinfection |
| Mycobacteria (M. tuberculosis) | 3-4 log10 | 60-120 seconds | Respiratory equipment disinfection |
| Enveloped Viruses (HIV, Influenza, SARS-CoV-2) | 4-5 log10 | 15-30 seconds | Surface disinfection, hand hygiene |
| Non-enveloped Viruses (Norovirus, Poliovirus) | 3-4 log10 | 60-120 seconds | Healthcare environmental cleaning |
| Fungi (Candida, Aspergillus) | 4-5 log10 | 30-60 seconds | Dermatological applications |
PVP-I products typically contain 7.5-10% PVP-I, providing 0.75-1.0% available iodine. This concentration represents the optimal balance between antimicrobial efficacy and tissue compatibility, validated through decades of clinical use.
Where Are the Most Critical Applications of PVP-I in Modern Healthcare?
PVP-I's versatility has established it as a cornerstone antiseptic across multiple healthcare domains. Its applications extend from routine procedures to specialized medical interventions.
Primary Medical Applications
- Surgical Antisepsis: Pre-operative skin preparation reduces surgical site infections by up to 50% compared to alcohol-only preparations
- Healthcare Worker Hand Hygiene: Surgical scrubs and healthcare personnel hand antisepsis
- Wound Management: Acute wound cleansing, burn care (partial thickness burns), ulcer management
- Mucous Membrane Antisepsis: Oral care, vaginal applications, ophthalmologic preparations
- Medical Device Disinfection: Catheters, endoscopes (when compatible with materials)
Specialized Clinical Uses
Beyond general antisepsis, PVP-I serves critical roles in:
- Neonatal Care: Umbilical cord care (reduces neonatal sepsis by 30-50%)
- Dermatology: Treatment of dermatological infections and pre-procedural skin preparation
- Dentistry: Pre-procedural mouth rinses, periodontal treatment, and oral surgery
- Ophthalmology: Pre-operative conjunctival antisepsis (lower concentration formulations)
- Emergency Medicine: Field wound care, disaster response, and emergency surgical preparation
What Key Advantages Does PVP-I Offer Over Alternative Antiseptics?
| Antiseptic Agent | Spectrum of Activity | Speed of Action | Residual Activity | Primary Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyvinylpyrrolidone Iodine (PVP-I) | Broadest (bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa) | Rapid (seconds to minutes) | Moderate (2-4 hours) | Staining, iodine sensitivity, inactivated by organic matter |
| Chlorhexidine Gluconate (CHG) | Primarily bacteria (excellent), limited viruses | Slower onset (minutes) | Excellent (up to 6 hours) | Poor against viruses, ototoxicity, corneal toxicity |
| Alcohol-based Solutions | Bacteria, enveloped viruses | Most rapid (seconds) | Minimal (evaporates quickly) | No persistent effect, ineffective on spores, dries skin |
| Hydrogen Peroxide | Broad but weaker than PVP-I | Variable (minutes) | None | Tissue toxicity at higher concentrations, unstable |
| Silver Compounds | Primarily bacteria, some fungi | Slow (hours for full effect) | Extended (days) | Limited spectrum, expensive, potential resistance |
PVP-I's dual mechanism—immediate microbial kill through free iodine combined with sustained release from the PVP complex—provides both rapid and prolonged protection. Crucially, after nearly 70 years of widespread clinical use, no clinically significant microbial resistance has emerged, a testament to its multi-target mechanism.
How Should PVP-I Be Safely Applied in Clinical Settings?
While PVP-I is generally safe when used appropriately, specific protocols optimize efficacy while minimizing risks.
Optimal Application Guidelines
- Skin Preparation: Apply to clean, dry skin. Use sufficient volume to cover area completely. Allow 1.5-2 minutes contact time before procedure.
- Wound Cleansing: Irrigate with PVP-I solution diluted as recommended (often 1:10 to 1:100 in sterile saline).
- Mucous Membranes: Use only approved formulations at appropriate concentrations (e.g., 1% for oral use, 2.5-5% for vaginal use).
- Healthcare Worker Hand Hygiene: Follow standardized surgical scrub protocols with 3-5 minute applications.
Critical Safety Considerations
| Safety Concern | Risk Level | Prevention/Mitigation | At-Risk Populations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iodine Absorption | Low for intact skin, Moderate for wounds/mucosa | Limit application area and duration; avoid large wound surfaces | Neonates, burn patients, thyroid disorders |
| Allergic Reactions | Rare (< 1% of population) | Screen for iodine allergy; have emergency protocol | Patients with seafood/iodine allergy history |
| Thyroid Effects | Low with proper use | Avoid prolonged large-area use; monitor in sensitive patients | Neonates, pregnant women, thyroid patients |
| Tissue Irritation | Low to Moderate | Use appropriate concentrations; avoid sensitive areas | Patients with sensitive skin, dermatitis |
| Inactivation by Blood/Organic Matter | High if not addressed | Clean area first; use sufficient volume; allow contact time | All applications in contaminated environments |
How is High-Quality PVP-I Manufactured and Controlled?
The production of pharmaceutical-grade PVP-I requires sophisticated manufacturing processes and stringent quality controls to ensure consistency, efficacy, and safety.
Manufacturing Process Overview
Leading manufacturers like Xiamen Aeco Chemical Industrial Co., Ltd. follow rigorous protocols:
- Polymer Synthesis: Production of precisely controlled molecular weight PVP (typically K-30: 40,000-55,000 Da)
- Complex Formation: Reaction with USP-grade iodine under controlled temperature and pH conditions
- Purification: Removal of uncomplexed iodine, heavy metals, and impurities
- Formulation: Preparation of final products (solutions, ointments, scrubs, powders)
- Quality Control: Comprehensive testing against pharmacopeial standards
Critical Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Test Method | Acceptance Criteria | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Available Iodine Content | Titration (USP method) | 9.0-12.0% w/w | Determines antimicrobial potency |
| Free Iodine | Spectrophotometric assay | < 0.5% of total iodine | Controls irritation potential |
| pH Value | Potentiometric measurement | 2.0-4.5 (solution) | Affects stability and compatibility |
| Heavy Metals | Atomic absorption spectroscopy | < 10 ppm total | Safety requirement |
| Microbial Limits | USP <61> and <62> | Sterile or within specified limits | Prevents microbial contamination |
| Viscosity | Viscometer | Product-specific range | Affects application characteristics |
Companies like Xiamen Aeco Chemical Industrial Co., Ltd. implement additional quality measures including batch traceability, stability testing under various conditions, and compatibility testing with common medical materials.
What Future Developments Are Expected for PVP-I Technology?
Despite its long history, PVP-I continues to evolve with innovations addressing current limitations and expanding applications.
Emerging Research Directions
- Enhanced Formulations: Nanoparticle-based PVP-I for deeper tissue penetration and sustained release
- Combination Therapies: Synergistic combinations with other antimicrobials to address specific resistant organisms
- Smart Delivery Systems: Environmental-responsive PVP-I formulations that activate under specific conditions (pH, temperature, enzymatic activity)
- Reduced Staining Variants: Molecular modifications to minimize cosmetic limitations without compromising efficacy
- Biofilm Penetration: Formulations optimized to disrupt and penetrate microbial biofilms
Market and Regulatory Trends
The PVP-I industry is increasingly addressing environmental considerations, including biodegradable formulations and reduced ecological impact manufacturing processes.
As antimicrobial resistance continues to challenge global health, PVP-I's proven efficacy and multi-mechanism action position it for continued relevance. The integration of traditional antiseptic wisdom with modern pharmaceutical technology promises to extend PVP-I's utility well into the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
A: Unlike iodine tincture which contains iodine dissolved in alcohol, PVP-I is a water-soluble complex that releases iodine gradually. This results in less irritation, reduced staining, and sustained antimicrobial activity. PVP-I is also more stable and has broader applications, including on mucous membranes where alcohol-based tinctures would be irritating.
A: Yes, PVP-I has demonstrated efficacy against SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing COVID-19. As an enveloped virus, it is highly susceptible to PVP-I. PVP-I mouthwashes/gargles have shown promise in reducing viral load in the oropharynx, and surface disinfectants containing PVP-I are effective against coronaviruses. However, it should complement rather than replace other preventive measures.
A: PVP-I attacks microorganisms through multiple simultaneous mechanisms—oxidizing proteins, halogenating nucleotides, and disrupting membranes. For resistance to develop, an organism would need to simultaneously evolve protection against all these mechanisms, which is evolutionarily improbable. This multi-target approach makes PVP-I particularly valuable in an era of increasing antimicrobial resistance.
A: Topical PVP-I on limited skin areas is generally considered safe during pregnancy. However, extensive application over large body surfaces or use on mucous membranes should be approached cautiously due to potential iodine absorption. Vaginal application before delivery is generally avoided as it may affect neonatal thyroid function. Always consult healthcare providers for specific medical advice.
A: PVP-I solutions should be stored in tightly closed, light-resistant containers at controlled room temperature (15-30°C/59-86°F). Exposure to heat, light, or air accelerates degradation. Brown glass bottles provide optimal protection. Once opened, solutions should be used within the manufacturer's recommended timeframe (typically 30 days for multi-use containers) to ensure maintained potency.
A: PVP-I should generally not be mixed with other antiseptics immediately before application, as chemical interactions may reduce efficacy. Specifically, hydrogen peroxide rapidly inactivates PVP-I by reducing iodine to inactive iodide. Sequential use (allowing one to dry completely before applying another) may be acceptable in some protocols, but combination products should only be used if specifically formulated and tested.
REFERENCES & FURTHER READING
- World Health Organization. (2018). WHO Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care. Geneva: WHO Press.
- Bigliardi, P. L., et al. (2017). "Povidone iodine in wound healing: A review of current concepts and practices." International Journal of Surgery, 44, 260-268.
- Kanagalingam, J., et al. (2015). "Practical use of povidone-iodine antiseptic in the maintenance of oral health." International Journal of Clinical Practice, 69(11), 1247-1256.
- Reimer, K., et al. (2002). "Antimicrobial effectiveness of povidone-iodine and consequences for new application areas." Dermatology, 204(Suppl 1), 114-120.
- United States Pharmacopeial Convention. (2023). USP Monograph: Povidone-Iodine. Rockville, MD: USP.
- Xiamen Aeco Chemical Industrial Co., Ltd. (2023). Technical Documentation: PVP-I Manufacturing Specifications and Quality Control Protocols.
- M. Eggers. (2019). "Infectious Disease Management and Control with Povidone-Iodine." Infectious Diseases and Therapy, 8(4), 581-593.
Note: This article was developed with research assistance from current scientific literature and AI analysis tools, which helped compile and organize the latest evidence-based information on PVP-I. All medical information should be verified with healthcare professionals for clinical applications.
Need High-Quality Polyvinylpyrrolidone Iodine?
For pharmaceutical-grade PVP-I manufactured to the highest international standards, consider products from established manufacturers.
Xiamen Aeco Chemical Industrial Co., Ltd. specializes in producing reliable, consistent PVP-I formulations for medical, pharmaceutical, and industrial applications. CONTACT US FOR PRODUCT INFORMATION. Our technical team can provide specifications, compatibility guidance, and application support for your specific requirements.
 English
English Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  العربية
العربية  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά