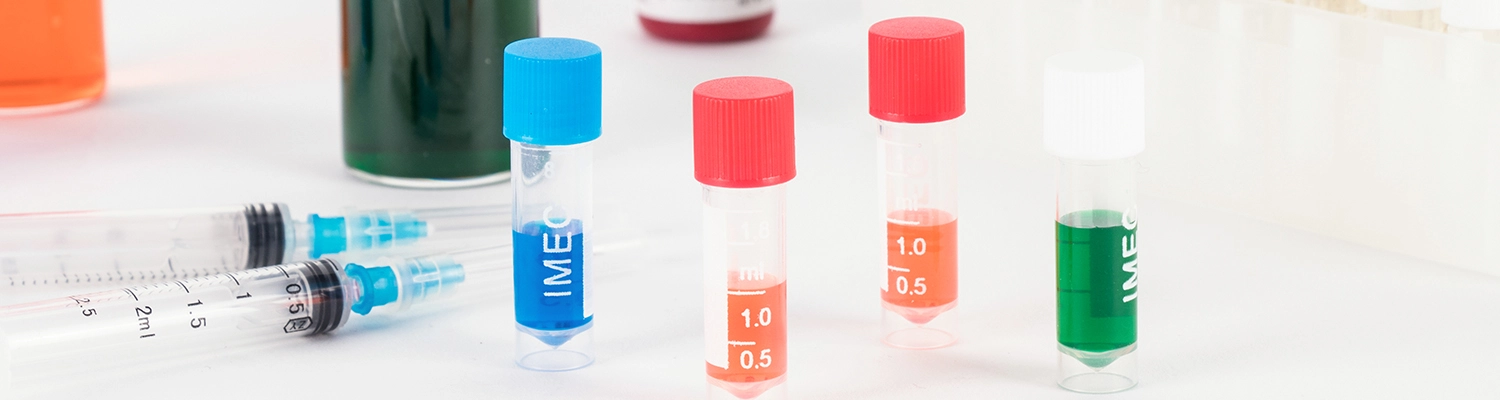
What is an intermediate according to chemistry?
In the field of chemical synthesis and industrial production, intermediates are the core link between raw materials and target products. This type of compound is neither the initial reactant nor the final product, but it plays an important role in connecting the upper and lower parts of the complex chemical reaction path. From laboratory research and development to large-scale production, the characteristics of intermediates directly affect the synthesis efficiency, cost control and product quality, and can be called the "invisible pillar" of the chemical industry.

The essence of intermediates: transition state carriers of the reaction process
Chemical intermediates are compounds from partial reactions of starting materials in multi-step synthesis. They need further transformation. Take aspirin synthesis. Before salicylic acid reacts with acetic anhydride to make acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), phenol goes through the Kolbe-Schmitt reaction. This makes sodium salicylate, a key intermediate. These substances often have unstable reactivity. Their structure has functional groups like hydroxyl and carboxyl. These groups need further modification via subsequent reactions. The goal is to get the target product’s molecular structure.
Classification of intermediates: Dual dimensions of function and application
According to the synthesis stage, intermediates can be divided into starting intermediates (such as ethylene and benzene, products of petroleum cracking), key intermediates (determining the core structure of the product, such as p-aminobenzene sulfonamide of sulfonamide drugs) and customized intermediates (designed for specific reactions, such as chiral drug intermediates). From the perspective of reaction type, intermediates can be divided into active intermediates (such as high-energy species that exist instantaneously, such as free radicals and carbon cations) and stable intermediates (which can be separated and stored for subsequent reactions). For example, Grignard reagent (RMgX), as a commonly used stable intermediate in organic synthesis, can construct complex carbon skeletons through nucleophilic addition.
The strategic value of intermediates in industrial production
In the pharmaceutical, pesticide, material and other industries, the application of intermediates significantly improves production efficiency. Enterprises can reduce the R&D cycle and trial and error costs by purchasing or preparing highly active intermediates. For example, in the production of liquid crystal materials, biphenyl intermediates of specific structures can be directly used as synthesis precursors to avoid the tedious steps of de novo synthesis. In addition, the standardized production of intermediates is conducive to industrial division of labor. Fine chemical companies focus on intermediate manufacturing, while downstream companies use them to complete the synthesis of terminal products, forming an efficient industrial chain collaboration model.
Frontier Trends: Green and Intelligent Technologies Reshape Intermediate Production
With the popularization of the concept of "green chemistry", intermediate synthesis is moving towards low energy consumption and less pollution. New technologies such as enzyme catalysis and photochemical synthesis can prepare high value-added intermediates under mild conditions, such as the selective synthesis of chiral pharmaceutical intermediates using biological enzymes, with an atomic economy close to 100%. At the same time, flow chemistry technology uses continuous reaction devices to achieve in-situ generation and transformation of intermediates, avoids resource waste in the separation and purification process, and promotes the upgrading of intermediate production to intelligent and modular.
As a "bridge material" for chemical synthesis, the research and application level of intermediates is an important indicator for measuring the technical strength of the chemical industry. In the future, with breakthroughs in technologies such as synthetic biology and artificial intelligence-assisted design, intermediates will play a greater role in the development of innovative materials, customized drug synthesis, and other fields, and continue to drive the high-quality development of the chemical industry.
 English
English Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  العربية
العربية  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά